LeetCode 407. Trapping Rain Water II
Priority Queue
Given the following 3x6 height map:
[
[1,4,3,1,3,2],
[3,2,1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,2,3,1]
]
Return 4.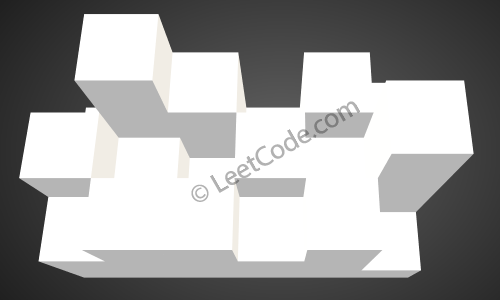
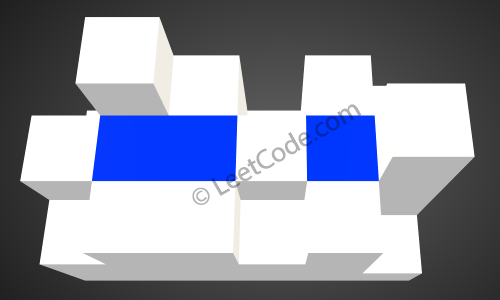
Solution
Last updated
Priority Queue
Given the following 3x6 height map:
[
[1,4,3,1,3,2],
[3,2,1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,2,3,1]
]
Return 4.

Last updated
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> que;
int row = heightMap.size(), col = heightMap[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited(row, vector<bool>(col, false));
int minimum = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (!(i==0 || i==row-1 || j==0 || j==col-1)) continue;
que.push({heightMap[i][j], i * col + j});
visited[i][j] = true;
minimum = min(minimum, heightMap[i][j]);
}
}
pair<int, int> dir[4] = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
int ans = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
pair<int, int> val = que.top();
que.pop();
int height = val.first;
int x = val.second / col;
int y = val.second % col;
minimum = max(minimum, height);
for (const pair<int, int>& d: dir) {
int nx = x + d.first;
int ny = y + d.second;
if (nx >= row || nx < 0 || ny < 0 || ny >= col || visited[nx][ny]) continue;
visited[nx][ny] = true;
if (heightMap[nx][ny] < minimum) {
ans += minimum - heightMap[nx][ny];
}
que.push({heightMap[nx][ny], nx * col + ny});
}
}
return ans;
}
};