LeetCode 1801. Number of Orders in the Backlog
Priority Queue
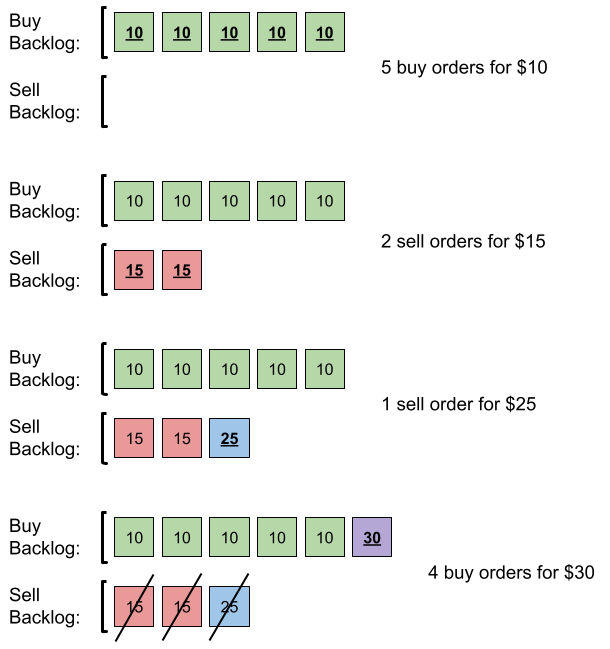
Input: orders = [[10,5,0],[15,2,1],[25,1,1],[30,4,0]]
Output: 6
Explanation: Here is what happens with the orders:
- 5 orders of type buy with price 10 are placed. There are no sell orders, so the 5 orders are added to the backlog.
- 2 orders of type sell with price 15 are placed. There are no buy orders with prices larger than or equal to 15, so the 2 orders are added to the backlog.
- 1 order of type sell with price 25 is placed. There are no buy orders with prices larger than or equal to 25 in the backlog, so this order is added to the backlog.
- 4 orders of type buy with price 30 are placed. The first 2 orders are matched with the 2 sell orders of the least price, which is 15 and these 2 sell orders are removed from the backlog. The 3rd order is matched with the sell order of the least price, which is 25 and this sell order is removed from the backlog. Then, there are no more sell orders in the backlog, so the 4th order is added to the backlog.
Finally, the backlog has 5 buy orders with price 10, and 1 buy order with price 30. So the total number of orders in the backlog is 6.Solution
PreviousLeetCode 1800. Maximum Ascending Subarray SumNextLeetCode 1802. Maximum Value at a Given Index in a Bounded Array
Last updated