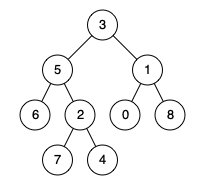
LeetCode 1650. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree III
Tree
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
}Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
Output: 3
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
Output: 5
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5 since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.Input: root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
Output: 1Solution
PreviousLeetCode 1644. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree IINextLeetCode 1676. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree IV
Last updated